Computer and Basics application of Computer
Computer and Basics application of Computer
Computers in the Era of Digitalization: Computers help us do all kinds of tasks either at or for personal use, as well are in professional work with great speed and efficiency. Computers are tools for serving special purposes: it can be used to write documents, and send these over an email or do some design work including the web designing as a whole lot of data that needs to go through may other operations before doing any task.

The post covers a broad scale introduction of computer, its fundamental concepts and components, including some common used software’s e.g. MS office, in-page, Internet browsing etc. Its the Intro to Computers Everything in […] Whether you are just starting with computers or looking to improve your knowledge, this guide will provide insight on how they work and what you can do with them.
Computer is an electronic device which process the data as per instructions (programs) and perform specific task. The core function of Tensor Flow is to carry out mathematical operations and these can store, access or directly manipulate the data using any kind in order to provide computational models required for calculations, decision-making as well as control capacity. A computer comprises hardware (physical components) and software (programs, data etc.) which working together do reading instructions to perform tasks like document processing, browsing the internet as well enables execution of applications.
Computer stands for
Computer is not an official acronym, but here are some creative expansions of the word “computer”.
Common
Operating
Machine
Particularly
Used for
Technical 
Education and
Research
The video is a whimsical interpretation and not an official definition. The term computer comes from Latin word “computer” means to calculate or compute. It originally described as a person who calculated figures manually.
Basic Components of Computer
A computer consists of several basic components that work together to perform tasks. These components can be divided into hardware and software. Here are the basic hardware components:
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The CPU is often referred to as the brain of the computer. It processes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data flow. It consists of two main parts:
- Control Unit (CU): Manages and controls the execution of instructions.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs mathematical calculations and logical operations.
-
Memory (RAM – Random Access Memory)
RAM is the computer’s short-term memory, used to store data and instructions that the CPU needs while performing tasks. It is volatile, meaning data is lost when the computer is turned off.
-
Storage (Hard Drive or SSD)
- Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or Solid State Drive (SSD): These are used for long-term storage of data, files, applications, and the operating system. Unlike RAM, storage retains data even when the computer is off.
- Motherboard
The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects all the components of the computer, including the CPU, memory, and storage. It also houses various input/output ports and connectors.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The PSU provides power to all components of the computer by converting electricity from the wall outlet into a usable form for the computer’s internal parts.
-
Input Devices
These devices allow users to interact with the computer by inputting data. Examples include:
- Keyboard: Used to enter text and commands.
- Mouse: Used for navigation and selection on the screen.
- Output Devices
These devices display or output the results of the computer’s processes. Examples include:
- Monitor: Displays visual output from the computer.
- Printer: Produces a physical copy of documents or images.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
The GPU handles rendering images, videos, and animations. It is crucial for gaming, video editing, and graphic design.
-
Input/output Ports
These are connectors that allow the computer to communicate with external devices, such as USB ports, HDMI ports, and audio jacks.
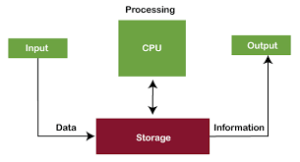
Block Diagram of Computer
A computer block diagram is a simplified representation of a computers major components as well as the way they interact. Figure 1: A typical block diagram of a computer
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Control Unit (CU): – its work is to control all the activities of computer.
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): It is used to perform arithmetic and logical operations.
Registers: Tiny, high-speed storage locations within the CPU where it can temporarily store stuff and churn through them.
-
Memory
RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary data and instructions for processes that the processor is currently working on. Volatile memory.
ROM (Read-Only Memory): A place to store instructions for the most important systems and in general it is written only once. Non-volatile memory.
- Storage
Primary Memory (RAM): Short-term memory storage, helps open the running files while working on it. Auxillary Storage Secondary Stores [Hard Disk Drive] HDD: Long term store for storing some Computers used applications and Operating System.
Solid State Drive (SSD): For next-gen storage to replace hard drives; this can also be used for longer-lasting data.
- Input Devices
- Keyboard: Used to input text and commands.
- Mouse: This is used for navigation and interaction with the GUI.
- Scanner: Sends hardcopy documents into a digital format.
- Microphone: Lists audio input.
-
Output Devices
- Monitor: Displays visual output from the computer.
- Printer: Produces physical copies of digital documents.
- Speakers: Output sound from the computer.
-
Motherboard
- System Bus: The communication pathway that connects the CPU, memory, and other components.
- Expansion Slots: For adding additional components like graphics cards, network cards, etc.
- Chipset: Controls the data flow between the CPU, memory, and peripherals.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Supplies power to all the components inside the computer.
- Communication Interfaces
Network Interface Card (NIC): Connects the computer to a network (e.g., Ethernet, Wi-Fi).
- USB ports allow the connection of external peripherals and storage devices.
-
Cooling System
- They help dissipate heat coming from the CPU and other hardware components.
There are several important qualities of computers which make them ideal to use for a variety of functions. Microsoft Windows Components of computer
-
Speed
Computers, on the other hand, current calculations and process data at very high speed (many times milliseconds or microseconds) Thanks to this, they are capable of accomplishing very complex actions instantly.
-
Accuracy
Computers do parallel operations with great precision and accuracy. As long as the instructions and hardware are working correctly they follow them verbatim which eliminates most human based errors.
-
Storage
So it can store large, huge amount of data and information in our computers. The data can be easily accessed, updated and deleted as required.
-
Automation
Once it is programmed then computer can do that type of work again and again. This diminishes the necessity of manual involvement and enhances efficiency.
- Versatility
Computers are personal computing devices, so they can handle different tasks from word processing and calculation to elaborate simulations or multimedia streaming.
Memory Units
Types of Memory different memory units in a computer used for data and instructions. The main memory units are:
-
Bit (Binary Digit)
Smallest unit of data in a computer (0 or 1)
-
Byte
Consists of 8 bits. It is the simplest type of data to store — a single character (letter, number or symbol).
-
Kilobyte (KB)
1 KB is 1024 bytes (2^10). Small data collection
-
Megabyte (MB)
1 MB = 1,024 KB (2^20 bytes). Mainly used to measure pictures or documents — storage of files being measured in the megabytes and over.
-
Gigabyte (GB)
1 GB = 1,024 MB (2^30 bytes). Measure storage capacities of hard drives, SSDs and bigger files.
-
Terabyte (TB)
1 TB = 1,024 GB (2^40 bytes). With the focus on capturing immense storage volumes, those SocialHistorica developers had tried to combine even &然 hain +Also only available for conveying mass storage levels
Zettabyte (ZB)
1 ZB = 1,024 EB (2^70 bytes). It is a scale of global data storage and internet data.
- Yottabyte (YB)
1 YB = 1,024 ZB (2^80 bytes). The big one, what you use to calculate up the biggest theoretical point of storage.
Types of Computer Memory
Primary Memory (Volatile)
RAM (Random Access Memory): A type of volatile memory used for data and instructions that the CPU is using at a given time. RAM is volatile so when you turn off your computer, everything stored in RAM will be lost.
Cache Memory: Volatile memory in much small area of CPU or close to the core with faster. It uses caches to cache data that is often called regularly.
Your Secondary Memory (Non-Volatile)
ROM (Read-Only Memory): Storage used to boot up the computer and basic hardware functions The data in ROM does not lose on power off and hence is nonvolatile.
HDD (Hard Disk Drive): Magnetic storage device that writes and reads data. It has large storage capacity and the most important of all, it is non-volatile.
SSD: A storage device which is faster than HDD, utilizes flash memory as a medium of data persistence. It is non-volatile and faster than HDDs when it comes to accessing data.
Tertiary and Off-line Storage
Optical Discs: For e.g. CDs, DVDs to store and distribute data.
Flash Drives: Portable flash-memory-based storage devices.
External Hard Drives: Adds storage and it is portable.